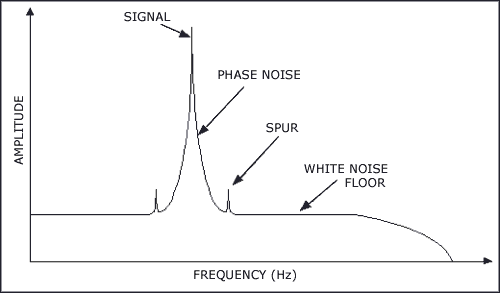
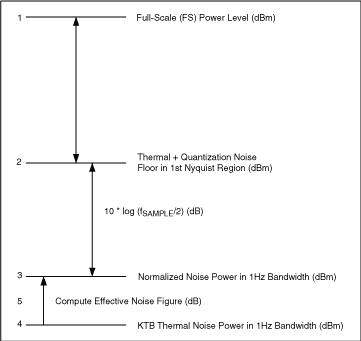
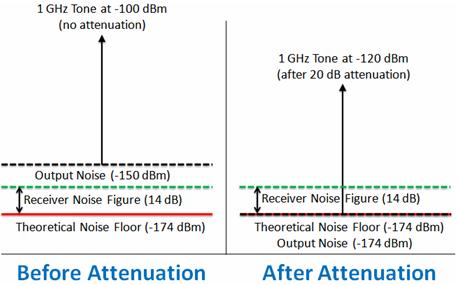
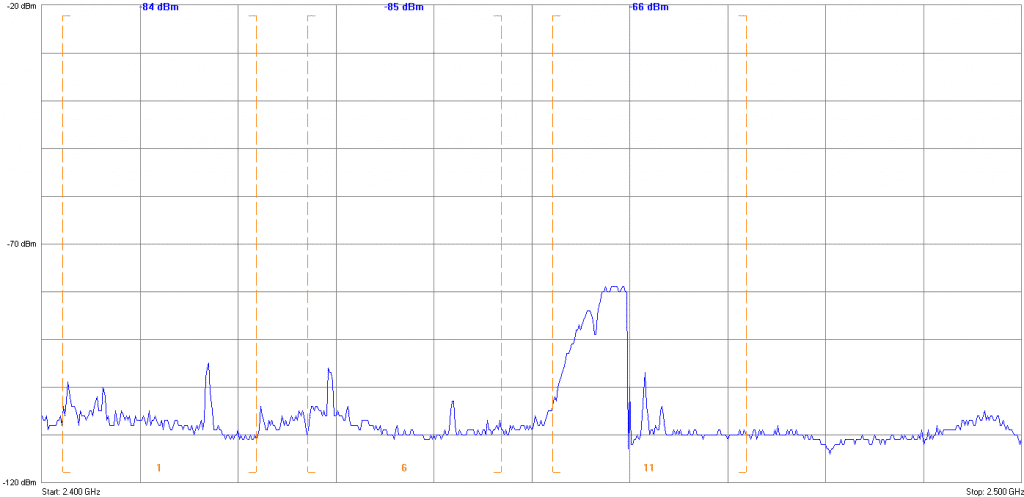
Noise floor calculator uncategorized june 10 2018 two birds home 0 what does noise figure signifies give temperature and lora sensitivity calculator factor versus propagation tutorial link budgets spectral density a new adc cascaded thermal.
Thermal noise floor equation.
Multiplying the equation to bandwidth gives the result as noise power.
This is most commonly calculated for a 1 hz bandwidth as it is easy to scale from here as noise power is proportional to the bandwidth.
Noise floor 174 nf 10 log.
Thermal noise power 173 96 dbm noise voltage 0 0008964 µv please note that temperature kelvin temperature celsius 273 16 thermal noise power and voltage equation.
V 4 1 3803 10 23 290 50 1.
Where n is the noise power and b is the bandwidth.
Noise voltage and power.
Careful control of noise components both in the design and operation of a ccd system is necessary to ensure that the signal level relative to noise is adequate to allow capture of accurate image information.
Thermal noise is unavoidable at non zero temperature see fluctuation dissipation theorem while other types depend mostly on device type such as shot noise which needs a steep potential barrier or manufacturing quality and semiconductor defects such as conductance fluctuations including 1 f noise.
The minimum equivalent input noise for a receiver at room temperature 290k is 174 dbm hz.
Calculating the noise power available in a one hertz bandwidth at a temperature of t 290 k defines a figure from which all other values can be obtained different bandwidths temperatures.
Thus the equivalent ntsc video input noise floor of any device is equal to 108 dbm fa where fa is its noise figure.
T 291 kelvin resistance 50 bw 1hz outputs.
1 hz noise floor.
It is then possible to calculate the noise floor for the receiver.
It is possible to calculate the thermal noise levels for room temperature 20 c or 290 k.
The noise resulting from thermal agitation of electrons is referred as thermal noise.
For any electronic measuring system the signal to noise ratio snr characterizes the quality of a measurement and determines the ultimate performance of the system.
Thermal noise is distinct from shot noise which consists of additional current fluctuations that occur when a voltage is applied and a macroscopic current starts to flow.
The most common impedance is 50 ω.